Lithium Salt Induces Phase Separation in Polymer Blend Electrolyte
Scientific Achievement
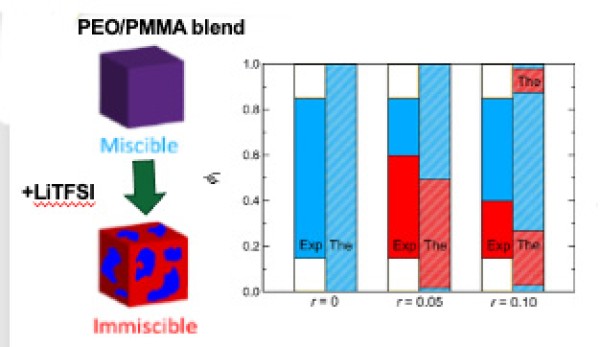
This work demonstrates that adding lithium bis(trifluoro-methanesulfonyl)imide (LiTFSI) induces phase separation in the normally fully miscible blend of poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO) and poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA).
Significance and Impact
The results will help in the design of novel polymer electrolytes with the desired immiscibility to yield both high mechanical stability and high Li-ion conductivity.
Research Details
- Small angle neutron scattering (SANS) determined the thermodynamic properties of PEO/PMMA/LiTFSI blend electrolytes.
- The de Gennes’ RPA framework was used to determine interaction parameters from x SANS scattering profiles of miscible blends.
- The results reveal an unusual relationship between miscibility, salt concentration, and blend composition.
“Thermodynamics and Phase Behavior of Poly(ethylene oxide)/ Poly(methyl methacrylate)/Salt Blend Electrolytes Studied by SmallAngle Neutron Scattering”
Neel J. Shah, Lilin He, Kevin W. Gao1, and Nitash P. Balsara1,
Macromolecules 56, 2889 -2898 (2023). DOI:10.1021/acs.macromol.2c02533