Structure of Ionomer Networks for Clean Energy Generation and Storage
July 18, 2024
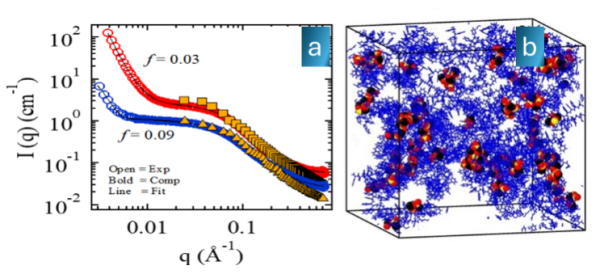
SANS profiles (left) of polystyrene sulfonate ionomers in toluene (blue and red symbols), calculated static structure factor S(q) from atomistic molecular dynamics computed networks (squares and triangles), at indicated sulfonation fraction (f). Fit of the data (solid lines) to a unified model of exponential functions, capturing features on hierarchical length scales. Visualization (right) of the computed networks (sulfur: yellow, oxygen: red, Na+: black, carbon: blue). Toluene not shown for clarity.
Scientific Achievement
The study revealed the multi-length scale heterogenous structure of polymeric networks, formed by assembly of ionizable groups.
Significance and Impact
Fundamental understanding of the formation of heterogenous ionizable polymeric networks elucidates the conditions required for making stable polymeric membranes for light-weight energy generation and storage.
Research Details
- Small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) was carried out on polystyrene sulfonate in toluene. A unified model was used to fit the data determining the hierarchical structure of the networks.
- A feedback loop was established between the exascale molecular dynamics (MD) simulation and SANS analysis.
“Clustering Effects on the Structure of Ionomer Solutions: A Combined SANS and Simulations Study.” Macromolecules 57 (4), 1688–1698 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.macromol.3c01646