Electronic Properties of the Bulk and Surface States of Fe1+yTe1−xSex
Scientific Achievement
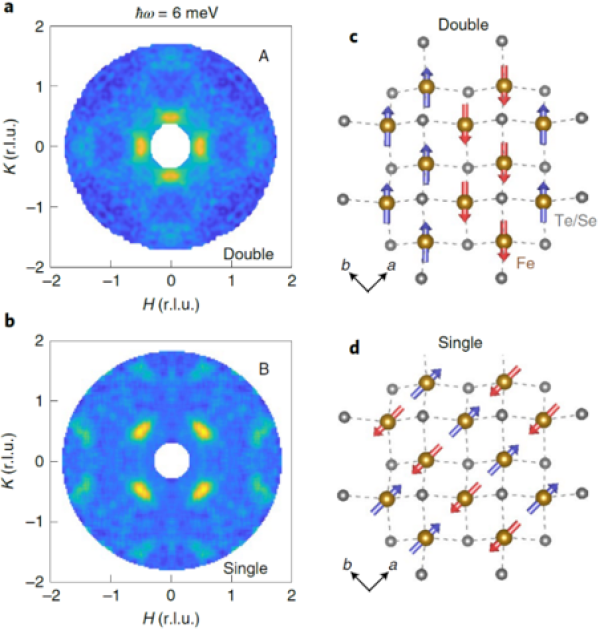
It is shown that in Fe1+yTe0.55Se0.45 superconductivity is found only at sufficiently low Fe concentration, is associated with single stripe antiferromagnetic correlations, and coexists with a topological surface state only with sufficiently high Te concentration.
Significance and Impact
These results point to the composition range necessary to achieve well-defined properties that are suitable for applications in topological quantum computing.
Research Details
- Polarized neutron scattering was used to probe magnetism and superconductivity in the bulk
- Angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy was used to probe electronic states near the Fermi energy.
- Energy dispersive x-ray spectroscopy and micro-voltage / current measurements were used to determine the local resistance and elemental composition.
"Electronic Properties of the Bulk and Surface States of Fe1+yTe1−xSex,"
Yangmu Li, Nader Zaki, Vasile Garlea, Andrei Savici, David Fobes, Zhijun Xu, Fernando Camino, Cedomir Petrovic, Genda Gu, Peter Johnson, John Tranquada, Igor Zaliznyak,
Nature Materials 20, 1221–1227 (2021).
DOI: 10.1038/s41563-021-00984-7