Hydration-induced Novel Chemical Expansion in Proton-conducting Oxides
July 18, 2024
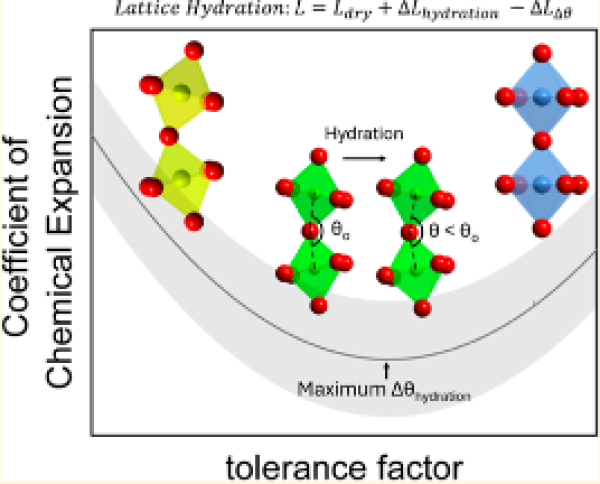
CCEs (determined from dilatometry and TGA measurements) plotted against tolerance factor for the compositions. Hydration induces the largest change in the Octahedral Tilt B-O-B angles leading to the minimum CCE
Scientific Achievement
A novel U-shape relationship between the hydration coefficients of chemical expansion (CCE) and tolerance factor in proton-conducting perovskite oxides has been discovered.
Significance and Impact
Understanding Hydration-induced strains in proton-conducting oxides is crucial for developing design principles for application in protonic ceramic electrochemical cells.
Research Details
- Hydration CCEs were determined from dilatometry and thermogravimetry (TGA) measurements
- In-situ neutron diffraction experiments in both Dry N2 and the humidified N2 condition (~1% H2O) were conducted
- Rietveld analysis of the POWGEN data revealed the hydration induced the largest change in the proton stoichiometry and Octahedral Tilt Angles.
“Tuning Perovskites’ Hydration-Induced Chemical Expansion with Octahedral Tilt Angles”, Lawrence O. Anderson, Qiang Zhang, and Nicola H. Perry.,
Chemistry of Materials 36 (12), 5953-5964 (2024)
DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.4c00354