Liquid-like Dynamics in a Solid-state Lithium Electrolyte
February 13, 2025
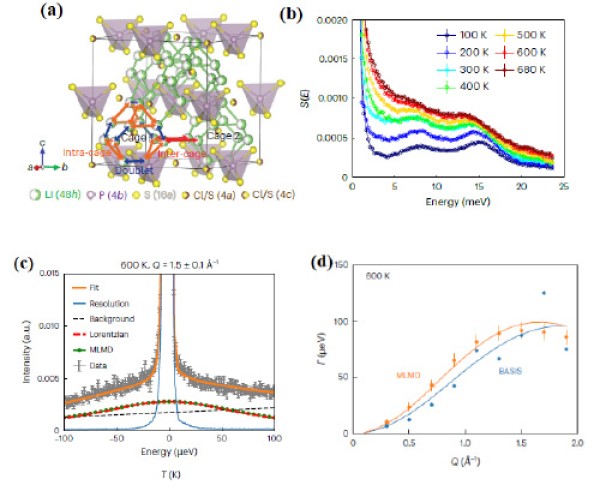
Fig. (a) Crystal structure of Li6PS5Cl (b) Dynamical structure factor S(E) at incident energy Ei = 25 meV as a function of temperature (c) QENS data with fit at 600 K (d) Chudley–Elliot fits at 600 K from BASIS (blue) and MLMD (orange)
Scientific Achievement
Fast, liquid-like hops of Li ions interact with the soft host lattice of the solid-state electrolyte (SSE) Li6PS5Cl to enable strong enhancements in ionic conductivity.
Significance and Impact
Superionic SSEs may be optimized through understanding the detailed lattice and ion dynamics, leading to better and safer future energy storage and conversion technologies.
Research Details
- Inelastic neutron scattering (INS) revealed liquid-like dynamics of Li ions at elevated temperatures, with vibrational density of states (DOS) proportional to frequency (ω) and emergent quasi-elastic broadening.
- Quasielastic neutron scattering (QENS) revealed the inter-cage hopping diffusion coefficient of 5.0 × 10−6 cm2s−1 with a jump length = 2.4 ± 0.4 Å, which matches the crystallographic inter-cage hopping distance.
- First-principles-based, machine-learned molecular dynamic (MLMD) simulations supported both the INS and the QENS results.
“Liquid-like dynamics in a solid-state lithium electrolyte,” Jingxuan Ding, Mayanak K. Gupta, Carolin Rosenbach, Hung-Min Lin, Naresh C. Osti, Douglas L. Abernathy, Wolfgang G. Zeier and Olivier Delaire. Nat. Phys. (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41567-024-02707-6