Magnetic Toroidicity in a Triangular Co2+-based Collinear Antiferromagnet
March 27, 2024
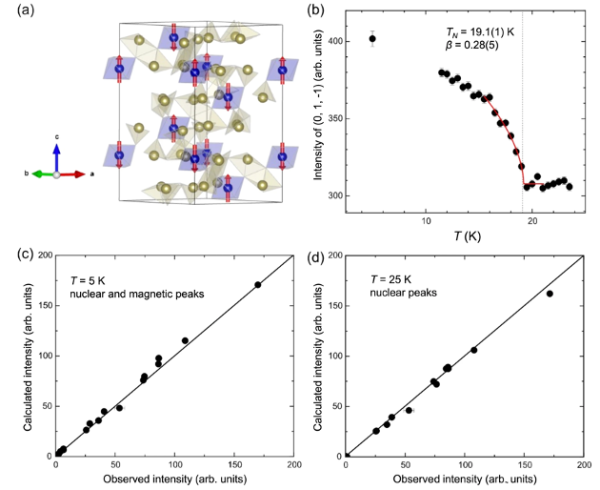
(a) Magnetic structure from single-crystal neutron diffraction. (b) Temperature evolution of (0, 1, -1) magnetic peak intensity. (c, d) Calculated vs. observed intensities (5K, nuclear & magnetic peaks) and (25K, nuclear peaks only), respectively
Scientific Achievement
A large off-diagonal magnetoelectric coefficient evidences magnetic toroidicity in CoTe6O13.
Significance and Impact
Collinear spins acting to induce toroidicity offer opportunities to design next-generation magnetoelectric materials with functional application potential.
Research Details
- Symmetry analysis suggests the existence of toroidal moments induced by locally canted collinear spins.
- Supporting temperature- and field-dependent dielectric permittivity measurements were performed.
Xianghan Xu, Yiqing Hao, Shiyu Peng, Qiang Zhang, Danrui Ni, Chen Yang, Xi Dai, Huibo Cao & R. J. Cava,
“Large off-diagonal magnetoelectricity in a triangular Co2+-based collinear antiferromagnet,”
Nature Communications 14, 8034 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-43858-z