Tunable Charge and Magnetic Orders in Kagome Antiferromagnetic Metal FeGe
July 15, 2025
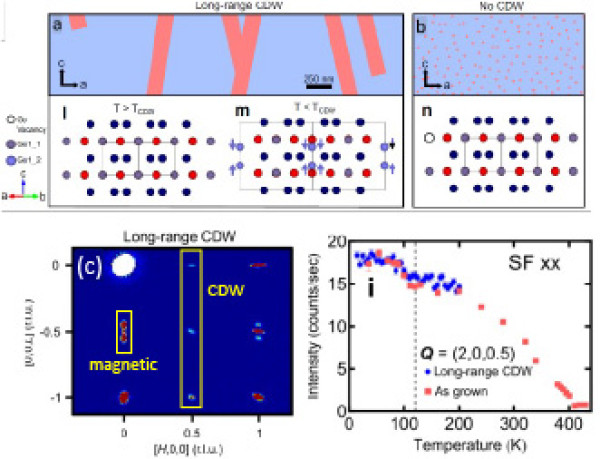
Red regions in (a) and (b) represent extended and uniformly distribute Ge vacancies, respectively. The coalescing of Ge vacancies in (a) enables formation of Ge-Ge dimers and long-range CDW order. (c) The sample annealed at 320oC shows both CDW and spin order at 6 K. (d) Polarized neutron data indicates an increase of magnetic moment below TCDW showing strong coupling between these states.
Scientific Achievement
Charge density wave (CDW), magnetic order and transport properties in FeGe are significantly influenced by annealing. This effect was found to originate from the distribution of Ge vacancies, which can be tuned through annealing.
Significance and Impact
The annealing tunable electric, magnetic and transport properties make FeGe a unique quantum material potentially useful for in-situ sensing and information transmission.
Research Details
- Transport, neutron scattering, scanning transmission electron microscopy and muon spin rotation measurements were conducted on FeGe crystals with various annealing conditions.
- Unpolarized and polarized neutron scattering studies revealed the annealing dependent CDW and magnetic structures.
“Vacancy-induced suppression of charge density wave order and its impact on magnetic order in Kagome”
Nature Communications 16, 3313 (2025) antiferromagnet FeGe
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-58583-y