Ion Electrosorption in Metal–Organic Frameworks (MOFs)
October 5, 2020
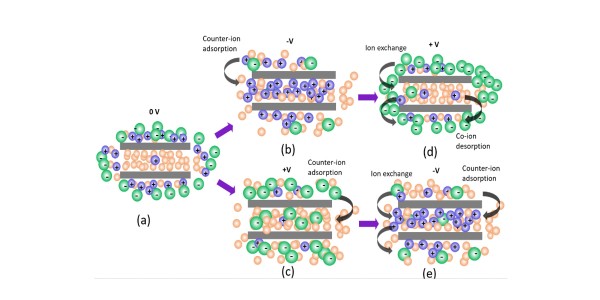
(a) In zero voltage, the DMF solvent (yellow) penetrates ionophobic nanopores, while electrolyte ions (Na+, green, CF3SO3-, purple) form a 30 Å layer on the surface. (b,c) With nonzero V, depending on the sign, either Na+ or CF3SO3- ions penetrate the pores via counter-ion adsorption. (d,e) Upon reversing the polarity, the ions rearrange by a combination of exchanging Na+ and CF3SO3- and adsorption which for negative voltages results in the DMF solvent being pushed out of the pores by Na+ ions.
Scientific Achievement
An applied voltage (V) causes electrolyte counter-ions to penetrate pores in MOFs via adsorption; Reversing V leads to switching of ions by ion exchange and adsorption.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the charge storage mechanisms in the MOF system shows the possibility of a new generation of highly efficient supercapacitors.
Research Details
- Samples were conductive Ni3(HITP)2 MOFs in deuterated dimethylformamide (DMF) solvent with the added electrolyte sodium triflate (CF3SO3Na) (HITP=2,3,6,7,10,11-hexaiminotriphenylene).
- The system was characterized in operando via small-angle neutron scattering.
- Additional characterization used powder X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy.
“Observation of Ion Electrosorption in Metal-Organic Framework Micropores with In Operando Small-Angle Neutron Scattering”
Lilin He, Luming Yang, Mircea Dincã, Rui Zhang, and Jianlin Li,
Angewandte Chemie International Edition 59, 9773 - 9779 (2020).
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201916201