Correlating Broadband Photoluminescence with Structural Dynamics in Layered Hybrid Halide Perovskites
Scientific Achievement
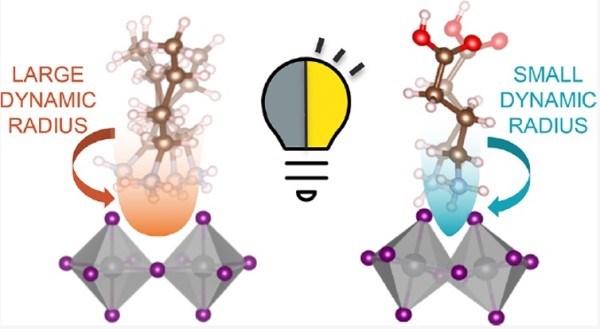
Measurements of rotational motions of the organic cations in layered hybrid halide perovskites (LHHP) show that a small effective dynamic radius is associated with increased out-of-plane tilt angles of the lead bromide octahedra.
Significance and Impact
Organic cation dynamics play a critical role in the structure and opto-electronic properties of LHHPs since large out-of-plane tilt angles are correlated with broadband emission that is desirable for solid-state lighting applications.
Research Details
- Quasi-elastic neutron scattering (QENS) was used to determine the organic cation dynamics in layered hybrid halide perovskites and modeled to extract the effective cation radii.
- Complementary photoluminescence, differential scanning calorimetry, and powder x-ray diffraction data was also collected.
“Correlating Broadband Photoluminescence with Structural Dynamics in Layered Hybrid Halide Perovskites”
Alexandra A. Koegel, Eve M. Mozur, Iain W. H. Oswald, Niina H. Jalarvo, Timothy R. Prisk, Madhusudan Tyagi, and James R. Neilson,
Journal of the American Chemical Society 144, 3 (2022). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.1c11217