ZnH-MOF Enables Hot CO2 Capture Relevant to Industrial Processes
December 14, 2024
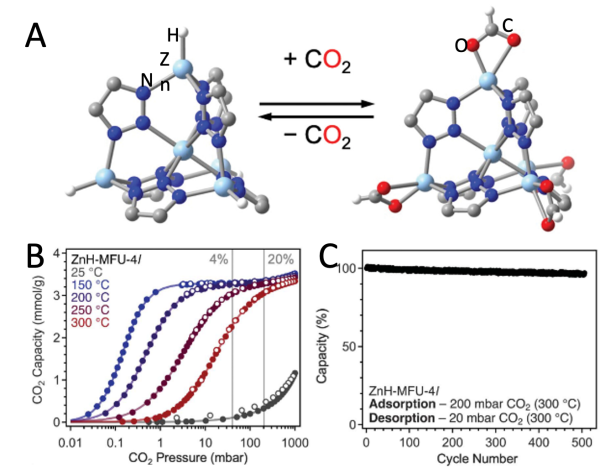
A) Reversible CO2 insertion into the Zn – H bonds. (B) Variable-temperature CO2 adsorption for ZnH-MFU-4l. (C) Cycling data for ZnH-MFU-4l through 508 isothermal adsorption and desorption cycles at 300°C, normalized to the first cycle, showing exceptional stability by retaining >96% of the initial adsorption capacity.
Scientific Achievement
Zinc hydride in a metal-organic framework, ZnH-MFU-4l, is shown to selectively, reversibly & robustly capture CO2 > 200°C.
Significance and Impact
This carbon capture technology can help limit CO2 emissions into the environment at relevant industrial operating temperatures. No other porous solid has been reported to reversibly capture CO2 at such elevated temperatures.
Research Details
- Crystal structure and CO2 uptake mechanism confirmed with nuclear magnetic resonance, Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, and single crystal x-ray and powder neutron diffraction.
- Isothermal adsorption measurements collected up to 300°C shows non-monotonic increase in CO2 uptake and capacity.
- Breakthrough measurements prove CO2 selectivity in dilute streams.
“High-temperature carbon dioxide capture in a porous material with terminal zinc hydride sites,” Science 386, 814-819 (2024).
Publication - https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.adk5697